DICS Pyramid, Data Governance, Traceability, Tags and Actions, or how to access Wisdom?
“True strength begins with wisdom.”
The DICS pyramid (for Data, Information, Knowledge and Wisdom) represents the entire data value chain.
More than just a data classification method, it could be presented as an objective for all corporate data governance. Apart from the objective, what means should be put in place to access it? How do you go from raw data to Wisdom?
A closer look at traceability and labels
The DICS Pyramid is a 4-level classification method:
Raw data (Data) : This refers to unstructured data such as text files, images, audio and video files, and so on. This raw data needs to be collected, stored and organized before it can be used effectively. It’s the company’s unmanaged data assets.
Information : Raw data is transformed into meaningful information using data analysis tools (using the Orkestra Framework, for example). This stage involves structuring, aggregating and contextualizing data to extract relevant information. A structured model is put in place here, around Datahub for example.
Knowledge : Information is transformed into knowledge using advanced modeling and analysis techniques. This stage involves identifying trends, patterns and relationships between data to derive actionable knowledge and information. It is the understanding of information which, among other things, enables its USE – (example with https://krialys.com/facturation/ )
Wisdom : Wisdom is achieved when knowledge is used to make decisions and guide actions. This stage involves using knowledge to solve problems, make decisions and improve processes. Data then becomes a true corporate strategy. From business data, data becomes corporate data.
Once you’ve set the goal of achieving wisdom, how do you get there? Implementing data governance, or data strategy, is the first step.
Data governance is the process of managing data efficiently and responsibly. Implementing effective data governance involves several key steps, which can be classified as Objectives & Priority, Organizations, Operational means and technical means.
Data governance, traceability & etiquette, why and how?
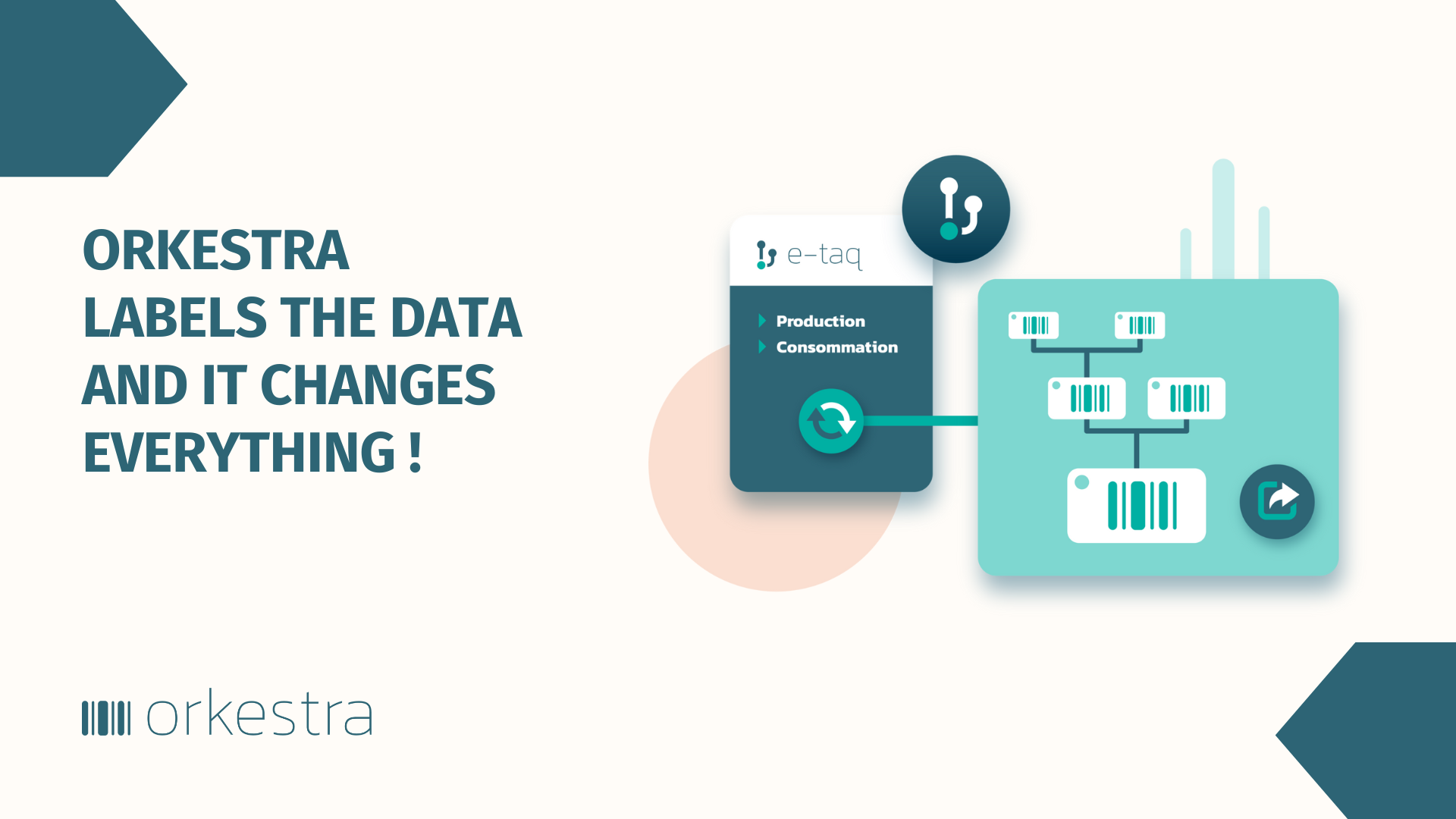
In practical terms, when it comes to serving data, operational resources need to be clearly defined upstream. One of these is essential: labels and their traceability. The key steps to successful implementation:
Define standards and policies : These should include rules and procedures for data use, management, security and confidentiality.
Label data : Labels can be used to identify data, indicating its level of confidentiality, ownership and relevance. Labels can also help track data through its lifecycle, from creation to deletion.
Define actions based on tags : Once data has been tagged, it’s important to define actions based on these tags. For example, if data is tagged as highly confidential, it can be protected with additional levels of security.
Set up monitoring and control processes : To ensure that labels and actions are applied correctly, it is important to set up monitoring and control processes. These processes can include regular audits to ensure that labels are correct and actions are implemented correctly.
Train employees : Employees need to be trained in data governance standards and policies, as well as in the use of tags and actions. They also need to be trained in monitoring and control processes to ensure that they fully understand their role in data governance.
In short, data tagging is a technique for assigning labels or tags to data to facilitate its search, organization and classification, thus guaranteeing its traceability, and its use in corporate data governance processes.
This data traceability is essential to ensure compliance, quality, transparency and informed decision-making. Companies striving to improve their data management should therefore consider data traceability a priority.
However, data governance is an ongoing process, so it’s important to remain vigilant and update policies and processes over time.